- 1Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Xinxiang Medical University, Xinxiang, China
- 2College of Public Health, School of Public Health, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
The prosperity of immunological therapy for cancer has aroused enormous passion for exploiting the novel targets of cancer immunotherapy. After the approval of blinatumomab, a bispecific antibody (bsAb) targeting on CD19 for acute lymphoblastic leukemia, a few of CD47-targeted bsAbs for cancer immunotherapy, are currently in clinical research. In our review of CD47-targeted bsAbs, we described the fundamental of bsAbs. Then, we summarized the information of four undergoing phase I researches, reviewed the main toxicities relevant to CD47-targeted bsAb immunological therapy of on-target cytotoxicity to healthy cells and a remarkable antigen-sink. Finally, we described possible mechanisms of resistance to CD47-targeted bsAb therapy. More clinical researches are supposed to adequately confirm its security and efficacy in clinical practice.
Introduction
Cancer is a serious health problem and the second primary cause of death all over the world. Data from the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) displayed that there were about 19.2 million new cancer cases and 9.9 million new cancer deaths in 2020. Over the past few decades, the introduction of cancer immunotherapies, aiming to ameliorate anti-tumor immune responses with less off-target effects, compared with chemotherapies and other agents which straightway kill tumor cells, has significantly improved the survival outcome of patients (1–3). Immunotherapeutic agents are designed to activate or modulate innate or adaptive immune system to assault cancer cells via repairing or enhancing natural mechanisms, plenty of which are escaped or damaged in the development of disease, thereby inhibiting tumor growth and metastasis (4–6). Results from the KEYNOTE-024 study on patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer revealed that the overall survival (OS) rate after five years was twice as high for patients that were treated with Keytruda (31.9%), compared to a chemotherapy regimen (16.3%) (7). Thus, immunotherapy is universally acknowledged to treat, and to heal, several kinds of cancer.
However, monotherapy with these and other drugs based on monoclonal antibodies cannot heal certain types of cancer, especially owing to T lymphocytes not actively participating in destroying tumors, nonetheless monoclonal antibodies merely restrain the combination of growth factors with the corresponding receptors. Monoclonal antibody interdicting the inhibitory signals which defend cancers from immune cells display fantastic outcomes while treating certain especial kinds of cancers. However, antibodies binding to two or more antigens (bsAbs), together with conjugated agents are research hotspots for chemo and radiotherapies.
Therapeutic BsAbs in Oncology
The original concept of bispecific antibody (bsAb) was proposed 50 years ago by Nisonoff and co-workers (8). Subsequently, the utilization of bsAbs to redirect immune cells to kill tumor cells was then certified in the 1980s, which provided a promising immunotherapeutic approach for cancer therapy and diagnosis (9). Blinatumomab (Blincyto®, CD3 × B lymphocyte antigen CD19) was the first bsAb to be ratified by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of relapsed or refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia (AML) in 2014 (10, 11). The remarkable success of blinatumomab has prompted pharmaceutical companies to efficiently generate and produce stable bsAbs. Till date, more than 100 bsAbs with different backbones and over 30 technology platforms have been reported and reviewed (12–16), and approximately, two-thirds of these bsAb therapeutics in the clinical pipeline are designated for the treatment in oncology (17), which either recruit and redirect the immune effector cells to kill cancer cells or interdict diverse signaling pathways via restraint of the ligand or the receptor (17–19).
BsAbs are genetically designed recombinant antibodies, which contain two disparate binding domains that allow simultaneous coupling with two diverse antigens or two diverse epitopes of the same antigen (Figure 1) (20, 21). Two diverse receptors or ligands on the surface of the same cell might be concurrently targeted by bsAbs, and they will give rise to restraint or stimulation of two diverse signaling pathways. Fusion of anti-tumor binding domain with the fragment crystallizable region (Fc) or the anti-CD3 binding domain is a conventional strategy to generate bsAbs, which has a great potential to recruit immune cells.
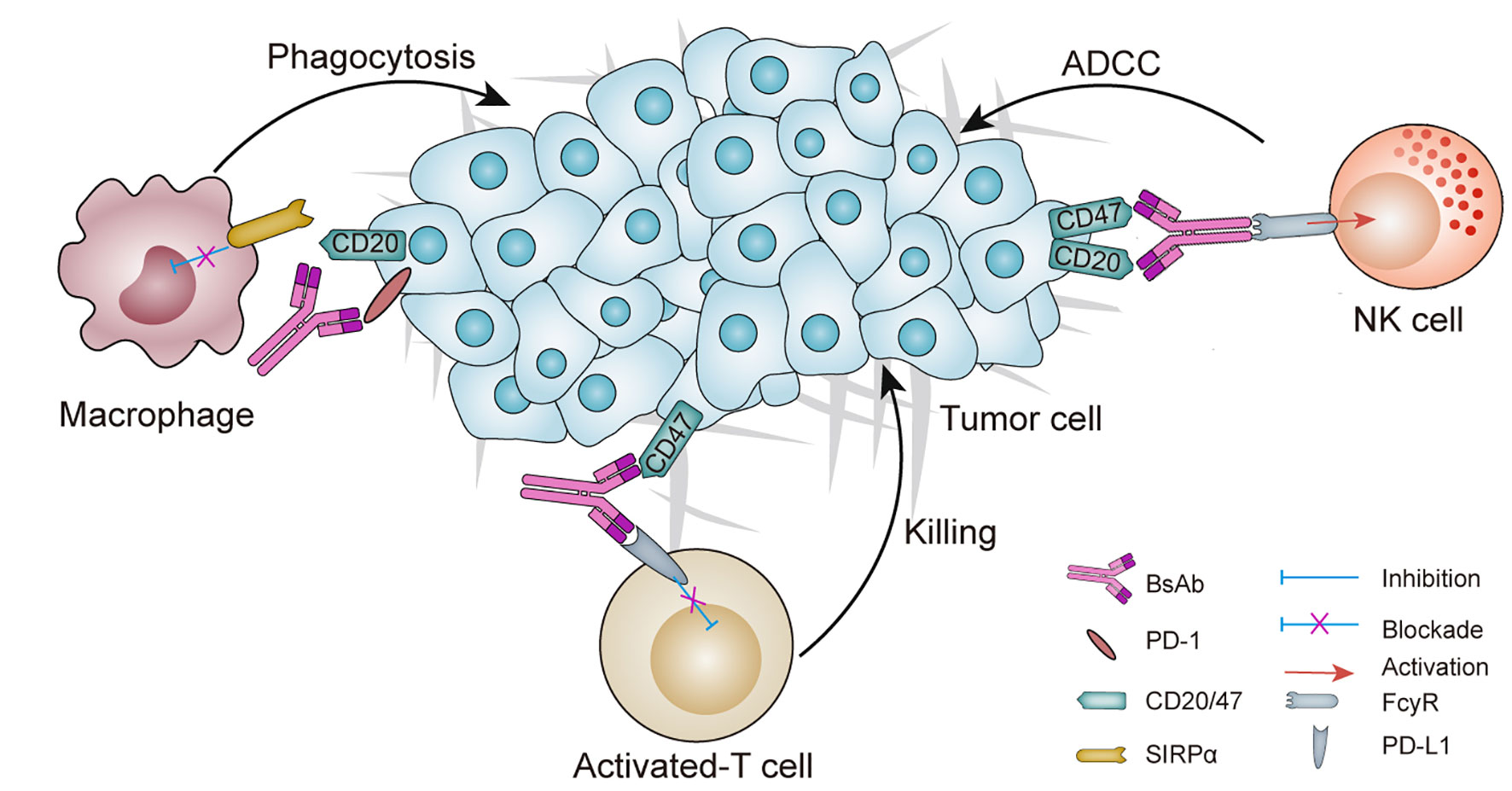
Figure 1 Schematic overview of a BsAb in cancer: mechanisms of action and potential targets. Dual checkpoints blockade is achieved by two-checkpoint blockers integrated into one antibody to inhibit two immune checkpoints simultaneously. Tumor targeted immunomodulators are designed for binding to one tumor-associated antigen (TAA) to inhibit TAA signaling pathway and the other immunomodulating receptor (e.g., PD-L1, CD47), thus regulating the immune system to attack the tumors. ADCC, antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity; bsAb, bispecific antibody; NK, natural killer; SIRPα, signal-regulatory protein α.
The bsAbs can be categorized into two different formats: a non-IgG-like format and an IgG-like format (Figure 2), and the structural elements of each format have implications for engagement and mobilization of the immune system. Among the clinically approved bsAbs, Catumaxomab and Hemlibra (emicizumabkxwh) have the IgG-like format, while Blinatumomab has the non-IgG-like format.
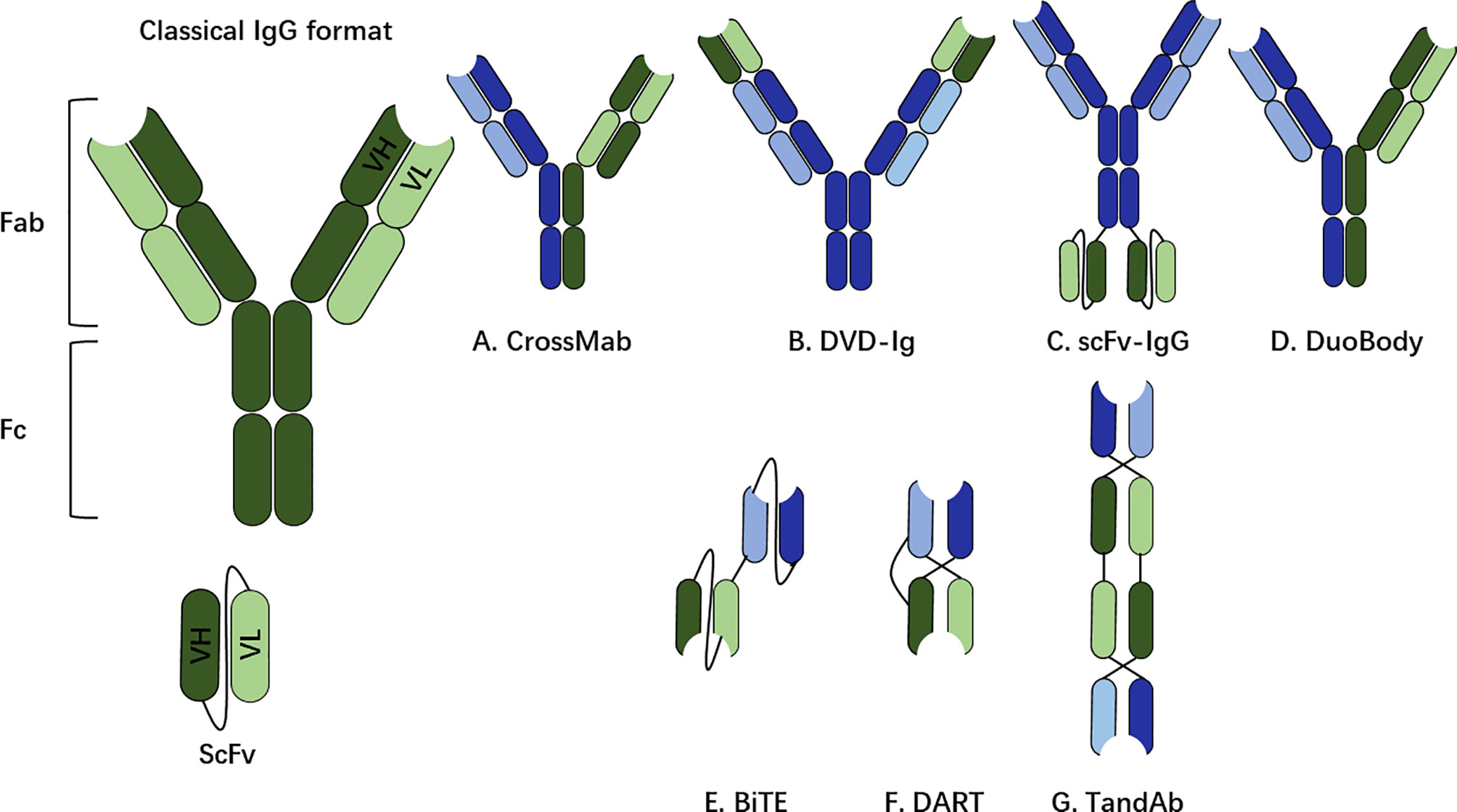
Figure 2 The non-IgG-like format and IgG-like format. The classical structure of a human immunoglobulin G (IgG) for reference, including fragment crystallizable (Fc) region and fragment antigen-binding (Fab). The binding part of the Fab region is called the single chain variable fragment (scFv), which is a synthetic protein composed of the heavy (VH) and light (VL) chains connected by a short peptide linger. (A–D) IgG-like bsAb formats (with Fc region). (E–G) non-IgG-like bsAb fragments (without Fc region). CrossMab Cross monoclonal antibody, DVD-Ig, dual-variable-domain immunoglobulin; scFv, single-chain variable fragment; BiTE, bispecific T-cell engager; DART, dual-affinity retargeting molecule; TandAb, tandem diabody.
The IgG-like bsAbs include the Fc region, which is an important determinant for bsAb in stimulating immune responses. Biochemical properties including affinity, glycosylation and isotype of the Fc region are responsible to trigger different immune effector cells. The Fc region triggers bsAb-mediated functionalities, including antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) and antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis (ADCP) (22).
Unlike the IgG-like bsAbs, the non-IgG-like bsAb format lacks the Fc region and in consequence, the molecular mass (30–50 kDa) is smaller than that of a whole IgG (150 kDa). Because the structure of a non-IgG-like format includes only VH and VL domains or the Fab fragment, such bsAb format depends only on Ag binding capacity for its therapeutic function. A major limitation of the non-IgG like bsAbs is their short-half life.
In contrast to antibody-drug conjugates and naked monoclonal antibodies (mAb), bsAbs can be engineered to recruit diverse effector immune cells through coupling with the membrane-associated antigen expressed from cancer cells, and the second antigen expressed in special immune cells, such as natural killer (NK) cells, effector T cells (23) or immunomodulatory proteins such as cluster of differentiation 47 (CD47) or programmed death receptors 1 (PD-1) (24). The superior effect might be ascribed to the tumor-directing function generated by bsAbs (25). Additionally, bsAbs execute their therapeutic effect by binding to receptors expressed on cell surface, without requiring for receptor internalization, which permits to target a disparate population of tumor antigens. A few of immunotherapies aiming to CD47, such as antibody-drug conjugates, chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells and bsAbs, are now undergoing assessed in clinical trials or preclinical studies. We have recently reported our experience of constructing a novel bsAb fusion protein both targeting EGFR and CD47, which could reduce the ‘‘off-target’’ effects because of CD47 expression on red blood cells (RBCs). Our study demonstrated that bi-SP with modified treatment indices may have a potential to treat CD47+ and EGFR+ cancers in the clinic (26).
Clinical Experience of CD47 as a Target for Cancer Immunotherapy
CD47 [Integrin-associated protein (IAP)] has a molecular weight of 45-55 kDa (Figure 3) with five-membrane-spanning segments in the membrane, which coprecipitates with platelet-derived β3 integrin and placental αvβ3 integrin (28). As we know, it is the receptor of thrombospondin family members, and is an extraordinary member of the membrane protein immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily with a single extracellular IgV-like region (29). CD47 is expressed at the plasma membrane of almost all cell types including mesenchymal stromal cells and blood cells, and is known to mediate vascular smooth cell proliferation and migration (30), platelet activation and spread (31), and recruit granulocytes and T cells to infections positions (32, 33). It was initially introduced as a tumor antigen involved in ovarian cancer, and multiple studies have indicated that CD47 is generally upregulated in various types of malignancies (34), such as myeloma (35), leiomyosarcoma (36), leukemia (37), non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (38), breast cancer (39), osteosarcoma (40), and hepatocellular carcinoma (41). It may be a mechanism of cancer immune evasion, and this mechanism-driving overexpression in tumor cells seems to be a compensatory response to a pro-inflammatory tumor microenvironment with high levels of TNF-α (42), which activates NF-κB signaling and thus regulates CD47 expression (43). Therefore, the CD47/SIRPα axis is considered as a novel existing target in immunology (39), and CD47 will have a major role in tumorigenesis, since its enhanced expression in cancer cells enables evasion of phagocytosis (44).
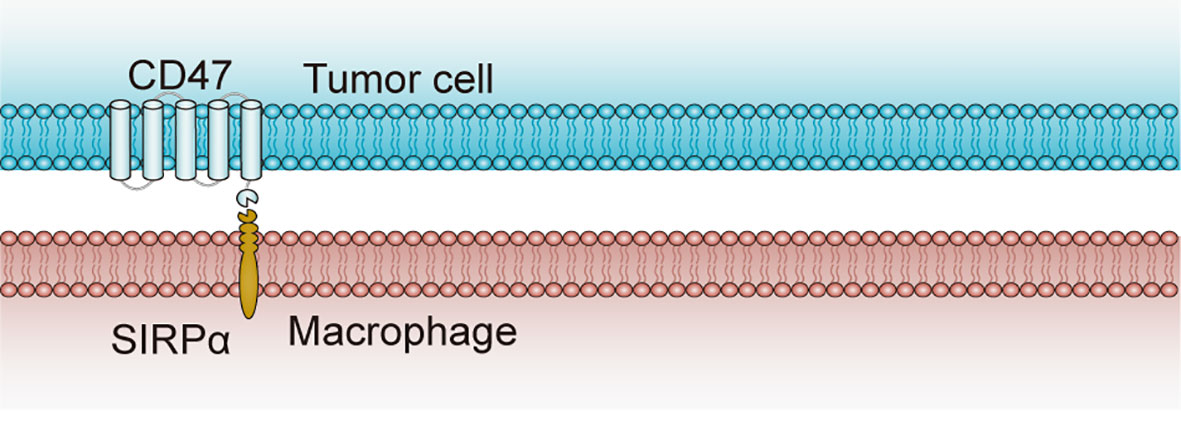
Figure 3 Structure and interaction of CD47 and SIRPα. CD47 contains one N-terminal extracellular IgV-like domain and five-membrane-spanning segments at the membrane. SIRPα, as the CD47 ligand, contains three extracellular IgSF domains, one transmembrane spanning region and an intracellular domain with ITIM motifs. CD47-SIRPα binding prevents the host cell from being targeted for phagocytosis, while anti-CD47 antibodies can block the suppression signal and promote phagocytosis by macrophages (27). CD47, cluster of differentiation 47; ITIM, immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif; SIRPα, signal-regulatory protein α.
Notably, CD47 sends “don’t eat me” signals by inhibiting phagocytosis of tumor cells and triggering an immune evasion and therefore serves as a myeloid-specific immune checkpoint when CD47 binds to signal regulatory protein α (SIRPα) that is an inhibitory receptor on macrophages and dendritic cells. In view of the interaction between CD47 and SIRPα in tumor cells restricts the anti-tumor immune response, treatment with anti-CD47 antibodies that restrain CD47 signaling in tumor cells was able to induce the phagocytosis of tumor cells by macrophages and stimulate anti-tumor immune responses in vivo (45). Consequently, a number of CD47-targeting antibodies are in clinical trials of numerous cancers spanning both hematological malignancies and solid tumors.
The most prominent clinically approved CD47-targeted immunotherapeutic is the humanized anti-CD47 antibody (Hu5F9-G4) that targets CD47 to induce phagocytosis, which was developed at Stanford University. Hu5F9-G4 is currently being assessed in phase I clinical research of patients with solid malignancies (www.clinical trials.gov identifier: NCT02216409). Also, HU5F9-G4 can trigger an effective anti-tumor T cell response, which cross-presents cancer cell antigens via macrophages, in order to provide protection against tumor recurrence.
A variety of ways have been established to target the CD47 pathway, such as directly interdicting of CD47 or its macrophage receptor SIRPα. Therefore, interdiction of CD47 in preclinical studies utilizing monospecific antibodies has shown promising effects. Nevertheless, the application of anti-CD47 antibodies still faces some safety risk issues. First, CD47 is ubiquitously expressed at the membranes of all cells, including RBCs, under normal and pathological conditions, generating cytotoxicity and antibody depletion. Therefore, comparing to traditional cancer immunotherapeutics, bsAbs targets CD47 along with other tumor antigens as a viable strategy for directing the synergistic benefits of combination therapy specifically toward tumor cells, has a potential to enhance security and efficacy. Secondly, anti-CD47 antibody monotherapy cannot completely get rid of lymphoma. In contrast, combination stratagems which induce adoptive immunity or refer to the utilization of anti-CD20 antibody, macrophage agonists, including IFN-c, interleukin-10, and other agents (e.g., caspase modulators and F-actin regulators), might possess enduring and efficient anti-lymphoma effects. Thirdly, the effects of diverse ways of interdicting CD47, including anti-CD47 antibodies or scFv derived from an antibody, are still uncharted.
BsAb Targeting CD47 and Other Targets That Are Currently in Clinical Trials in Oncology
BsAbs co-targeting CD47 and other tumor-specific antigens may improve the binding specificity of CD47-directed antibody, thus enhancing safety and efficacy. Considering these above, bsAbs targeting tumor-specific receptors possessing high binding affinity on one arm and CD47 with lower affinity on the other arm, are nowadays being assessment in clinical trials or are in preclinical study. There are currently four bsAbs constructs targeting CD47 for the treatment of patients with various kinds of cancers, which are undergoing assessed in the clinics at present (Table 1).
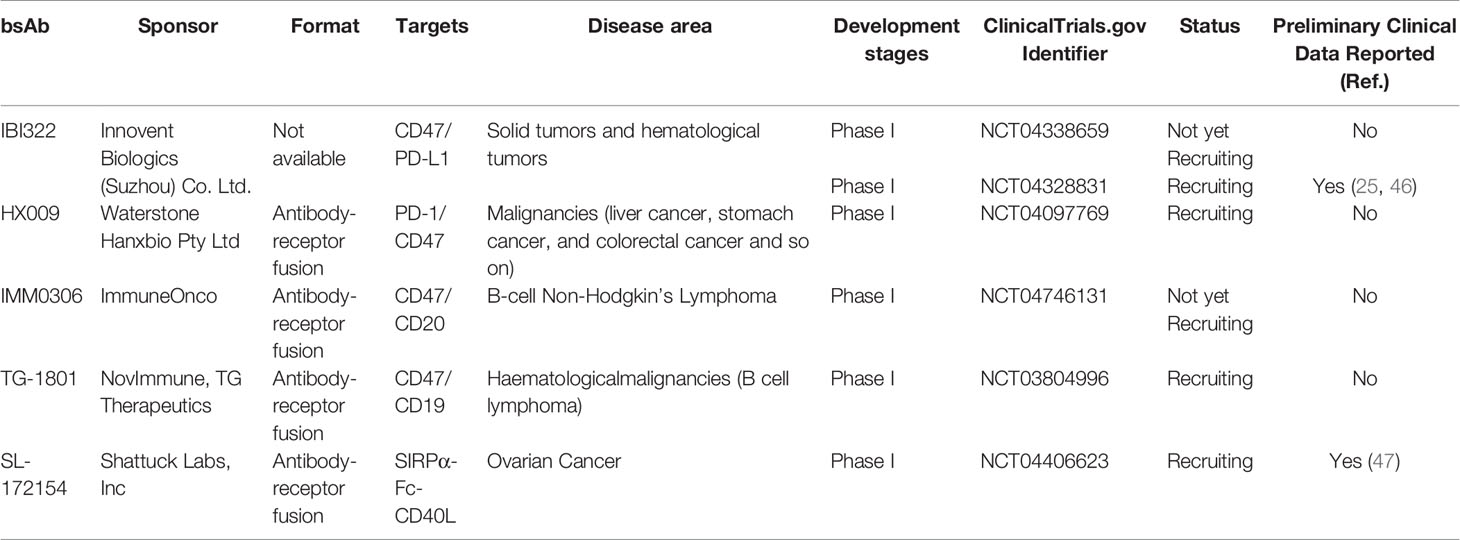
Table 1 CD47-targeted bsAbs in clinical trials as of March 2021 (44).
IBI322
IBI322 is the first anti-CD47/PD-L1 checkpoint bsAb that inhibits both the PD-1/PD-L1 and CD47/SIRP-α pathways, which is used for the treatment of patients with advanced malignancies (25). Preclinical studies have demonstrated that IBI322 can effectively block CD47/SIRP-α interaction and induce macrophages to phagocytose CD47-expressed tumor cells, which is equivalent to anti-CD47 monoclonal antibody. And it was suggested that the affinity of IBI322 to PD-L1 was stronger than that to CD47, implying a potential therapy regime in PD-L1-positive cancers (48). IBI322 also effectively blocks the binding of PD-1 to PD-L1 and activates CD4+T lymphocytes, which is comparable to anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody. Since PD-L1 is expressed in tumor cells, IBI322 can selectively bind to tumor cells more effectively than anti-CD47 monospecific antibody, thus reducing the possibility of binding to CD47 expressed on RBCs, which could ultimately reduce the toxicity associated with anti-CD47 antibodies. Therefore, IBI322 has stronger anti-tumor activity and higher safety profile.
The first case had been triumphantly administrated in a Phase I clinical trial (CIBI322A101) of the promisingly first-in-class recombinant anti-CD47/PD-L1 bsAb (IBI322) in China. CIBI322A101 is a Phase Ia/Ib clinical study conducted in China to evaluate IBI322 in the treatment of patients with advanced malignancies. Meanwhile, dose selection for first-in-class human (FIH) studies of IBI322, authorized by the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) for clinical trials (IND No. CXSL1900125) was evaluated, suggesting that the preliminary pharmacodynamics (PD) study with 0.34 mg/kg was rational (46). For scientific confirmation, it still needs more researches at different doses to be conducted in future.
Anti-CD47 antibodies have the tendency to attack normal cells. However, IBI-322 is preferentially distributed in PD-L1-positive tumor cells, thus decreasing the possible adverse effects of this target associated with monospecific anti-CD47 antibodies (25). In addition, bispecific monoclonal antibody enhances cytotoxicity, antibody selectivity and functional affinity by targeting effector cells directly to tumor cells. Preliminary results showed that IBI322 had higher efficacy in vivo, tumor-rich distribution and better safety than the mono-specific anti-CD47 antibody (25). Bispecific antibody could offer a lower-cost solution for patients compared with two monoclonal antibody combinatorial therapies. Therefore, the development of the anti-CD47/PD-L1 bsAb will provide patients with a novel, comprehensive, effective, and cost-saving treatment regimen. IBI322 has the potential to benefit more patients in need. Given that IBI322 is currently undergoing a phase I dose escalation trials in China (NCT04328831) and USA (NCT04338659), there is no clinical data reported for it. In China, CIBI322A101 is a Phase 1a/1b clinical study conducted to evaluate IBI322 in the treatment of patients with advanced malignancies. The Phase 1b study will be carried out to evaluate the efficacy of IBI322 in lung, cervical, esophageal, head and neck squamous cell and liver carcinomas. Collectively, more clinical studies are needed still in the clinic.
HX009
As crucial innate and adaptive immune checkpoints on cancer cells, CD47 and PD-L1 coordinate to inhibit immune sensing. Preclinical studies have demonstrated a bsAb co-targeting PD-L1 and CD47 (49) dramatically improved tumor targeting and treatment outcome vs. monotherapy in vitro and in vivo. Anti-PD-1 antibodies restored large amounts of exhausted T cells and anti-CD47 antibodies stimulated phagocytosis of macrophage. Based on this, the anti-PD-1/CD47 bsAb, HX009, was developed by Hangzhou Hanx Biopharmaceutics, Inc. (HanxBio), to treat patients with advanced solid tumors, including gastric cancer, colorectal cancer and liver cancer. Consisting of human IgG4-Fc region of anti-PD-1 mAb and extracellular domain (ECD) of SIRPα, it achieves the synergistic anti-tumor effects by simultaneously activating both innate and acquired immune responses to suppress tumor immune escape and release immune suppression at immune checkpoints.
This antibody-receptor fusion format may have time-cost savings by adapting the natural receptor to the bsAb over the two mAbs-based bsAb for which one more mAb has to be developed. However, due to relatively lower stability of the receptor portion, the antibody-receptor fusion proteins might suffer less stability than the bsAbs based on two mAbs. Currently, HX009 is in early phase I clinical trial (NCT04097769) for patients with advanced solid tumors. So far, no clinical data has been reported for safety and efficacy of HX009.
IMM0306
IMM0306, developed by Shanghai ImmuneOnco Biopharmaceuticals Co. (ImmuneOnco), is a bispecific recombinant antibody-receptor fusion protein. It is designed to target both CD47 and CD20 on B cells but avoid binding to human RBCs, which could simultaneously act on the tumor disease targets and modulate the immune system. By activating the phagocytosis potency of macrophages and triggering antigen-specific T cells via tumor antigen presentation, IMM0306 will become a new hot point in the research of cancer immunotherapy in future (50).
Extensive characterization in vitro demonstrated that IMM0306 binds to both CD47 and CD20 with affinity 3-8 folds lower than either single-targeted molecule. However, it has greater pro-phagocytosis activity over CD47-positive target cells, and even stronger ADCC activity than Rituximab (an anti-CD20 mAb). Intriguingly, IMM0306 has no binding activity at all toward human RBCs, albeit much lower binding activity toward monkey RBCs (51). Treatment of tumor-implanted SCID mice with IMM0306 significantly inhibited tumor growth and led to eradication of the tumor cells from 5 out of 8 mice, which is much more effective than Rituximab (51). Besides, the in vivo studies demonstrated that IMM0306 did not bind to human RBCs and did not induce T cell apoptosis. It can clear lymphoma at a low dose (1.5 mg/kg) (52), showing obvious advantages in safety and clinical development. Preclinical study in non-human primates demonstrated a favorable pharmacokinetic profile with no obvious hemotoxicity following single as well as multiple administrations at different dosage.
All these studies above suggest that antibody-trap like IMM0306 might be an ideal approach for CD47-targeted immunotherapy development since selective avoidance of RBCs mediated antigen-sink as well as anemia could be achieved along with the robust anti-tumor activity. In addition, the preclinical studies confirmed that IMM0306 achieved significant therapeutic effects in various tumor models. IMM0306 is now being assessed in phase I trial (NCT04746131) for the evaluation of safety and effect in patients with B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Meanwhile, dose selection of IMM0306, authorized by NMPA for clinical trials (IND No. CTR20192612), is being evaluated for patients with refractory or recurrent CD20 positive B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Until now, there is no clinical data reported for IMM0306.
TG-1801
As the first-in-class anti-CD47/CD19 bsAb, TG-1801 is a fully humanized IgG1, targeting the ‘don’t eat me’ self-defense signal which defends cancer cells against the immune system. This bsAb is designed by combining a low-affinity CD47 targeting antibody with a high-affinity antibody against CD19, to make sure that CD47 is employed by the bsAb only on tumor cells that co-expressed both antigens. It has an enhanced Fc-mediated phagocytosis and reserved its activity while the existence of high levels of non-tumor-associated CD47 (53). TG-1801 is designed to selectively target CD47 on CD19+ B cells, sparing RBCs and platelets, with the blockade of CD47-SIRPα macrophage checkpoint on mature B cells. It will avoid off-target toxicity, representing a novel immunological therapeutic strategy with potential for synergistic or complimentary activity with drugs in the current pipeline. In addition, the co-targeting of CD47 and CD19 enhances the expected safety, as well as induces antibody dependent cytotoxicity (ADCC) by retaining the function of its IgG1 Fc region, thereby providing a second mechanism for anti-tumor activity.
To conclude, TG-1801 might play a crucial part in improving the outcome of patients with B cell malignancies. Meanwhile, TG Therapeutics first demonstrated the synergistic effect of TG-1801 in combination with ublituximab (anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody) and umbralisib (PI3K-δ/casein kinase-1ϵ inhibitor) (54), and the synergistic tumor growth inhibition appeared to be mediated by increased infiltration of immune effector cells (55). At present, TG-1801 is undergoing assessment in Phase I trial (NCT03804996) to evaluate its safety and efficacy for treating patients with B cell lymphoma. Thus far, there is no clinical data reported for TG-1801.
SL-172154
SL-172154, developed by Shattuck Labs Inc., is a novel fusion protein consisting of human SIRPα and CD40L (SIRPα-Fc-CD40L) linked via a human Fc. It is designed to block the CD47 immune checkpoint while simultaneously activating the CD40 pathway through the dual mechanism, which are both checkpoint blockade and TNF activation. Being one of bifunctional fusion protein candidates, SL-172154 is developed through Shattuck Agonist Redirected Checkpoint (ARC) Platform Technology, which is designed to solve structural limitations. Previous studies found that SL-172154 significantly improved rejection of both primary and secondary tumors, as compared with individual antibodies targeting CD40 and CD47 used alone or in combination, similar to PD-1-Fc-OX40L (56). Notably, the safety and efficacy of the bsAb in nonhuman primates in vivo that, the bsAb stimulated dose-dependent elevation in multiple serum cytokines and CD40+ B-cell margination in cynomolgus macaques, without causing hemolysis or thrombocytopenia, provides justification to further explore this strategy in patients with cancers (47).
Currently, SL-172154 is being evaluated in a phase 1 trial (NCT04406623) for patients with ovarian cancer. So far, no clinical data has been reported for safety and efficacy of SL-172154.
Biosafety Concerns and Future Directions Associated With CD47-Targeted BsAbs
Given the huge potential of anti-CD47 bsAbs, there is ongoing interest in expanding this field in cancer immunotherapy and several bsAbs targeting CD47 have entered into clinical trials. So far in current phase 1 studies, blast reduction and complete remission rates have been observed, although safe targeting doses to be used in future phase 2 clinical trials still need to be determined for each bsAb targeting CD47 construct. Despite ubiquitously expressed on almost all cell types, on-target cytotoxicity of CD47 to healthy cells and a prominent antigen-sink phenomenon have influenced the development of CD47-targeting agents (57). Therefore, it is important to improve our understanding for potential biosafety problems.
Since CD47 is ubiquitously expressed, potential problems with anti-CD47 antibodies as anticancer agents were possible off-target effects such as anemia (58). CD47 is a crucial regulator of RBCs turnover (59). Buatois et al. (60) indicated that Hu47F9-G4 alone or in combination with other antibodies may cause accidental killing of normal RBCs, potentially resulting in anemia. Hence, there are concerns that CD47-targeting antibodies would expedite RBCs clearance and cause hemolytic anemia since several agents in this class have learn about RBC affinity while others do not. For CD47-targeting bsAbs in preclinical research, various methods are being used to attempt to alleviate this on-target cytotoxicity. For example, the NHP study indicated that a second dose of IBI322 (25) resulted in an extra less drop in the RBCs and hematocrit indices. While RBC counts of both groups began to revert on day 11, IBI322 treatment resulted in a dramatically enhanced RBC count, compared with the Hu5F9 group on day 15. Given that the cross-reaction of IBI322 with cyno PD-L1 and CD47 at approximate affinities to receptors, it is rational to expect that IBI322 could decrease CD47 target-mediated side-effect in patients. CD47 might become an efficient target of this stratagem soon afterward. Comprehensive assessment of IBI322 for the safety and efficacy is necessary in future.
Notably, CD47-targeting agents (i.e., Hu5F9-G4 and TTI-621) could cause acute anemia and thrombocytopenia in people (61–63), which might as well as depend upon the Fc format. The toxicity of anti-CD47 antibodies appears to be Fc-dependent, given that anti-CD47 antibodies, and SIRPα-Fc fusion proteins give rise to this toxicity, while high-affinity SIRPα monomers do not (39, 64, 65). These findings suggest that further studies should aim to optimize the structure of the anti-CD47 bsAbs when attempting to design novel drugs without unwanted side-effects. How to reduce or avoid damage to normal cells while exerting antitumor effects is one of the problems that needs to be considered when designing anti-CD47 therapeutics.
In addition, the expression of CD47 on normal tissues may create an ‘antigen sink’ that prevents anti-CD47 therapeutic antibodies from reaching tumor cell targets in vivo, which also pose a problem in the development of anti-CD47 bsAbs. One strategy to circumvent this issue is by reducing the bsAbs affinity for CD47 but retaining the ability to block the CD47-SIRPα interaction and elevating the affinity to a second tumor antigen. In future studies, more strategies by targeting CD47 and its ligands specifically on tumor cells should be investigated.
Upon macrophage or dendritic cell-mediated phagocytosis of cancer cells by CD47 blockade, these phagocytes may present tumor antigens to T cells to induce anti-tumor T cell responses (66, 67). Therefore, the regimen by combining with T-cell checkpoint inhibitors (with anti-PD-1 or PD-L1 agents) may further augment T cell responses and enhance efficacy. Several pre-clinical studies have demonstrated that CD47 blockade in combination with T cell checkpoint inhibitors can enhance antitumor activity (68–70). Importantly, CD47-targeting agents have the potential to augment existing antibody therapies by adding the benefit of blocking the CD47-mediated inhibitory signal to the established therapeutic effect of pro-phagocytic antitumor antibodies.
We should realize that future improvements in cancer screening and precision medicine will enable the identification and stratification of specific tumor types and/or stages of cancer that would be most amenable to treatment with a certain type or types of anti-CD47 treatment.
Conclusion
Recently, we have witnessed much progress with bsAb technologies and therapeutics as reviewed here and elsewhere (13, 71), which have found wide applicability to immunotherapy for cancer treatment. And thus, many bsAb constructs with differing mechanisms of action are being investigated, each with their own limitations and advantages. In this review, we summarized diverse strategies of cancer immunotherapy and characterized the breakthrough in bsAbs development which might be devoted into enhancing the treatment effect and decreasing untoward effects, which mark the beginning of a new era for cancer immunotherapy. Although cancer immunotherapy is rapidly advancing, the effectiveness of bsAbs, especially CD47 bsAbs, can vary between different cancer types, different studies, and even different cancer types, in other words, the therapeutic efficacy of anti-CD47 agents may be tumor specific. Thus, the exploration of novel strategies by targeting macrophage checkpoints is under development. In addition to CD47/SIRPα-targeting antibodies and fusion proteins, the other potential CD47-directed strategies should also be considered.
In summary, two exclusion conditions must be set in the anti-CD47 bsAbs screening process: 1) RBC binding and erythrocyte agglutination induction; 2) Induction of T lymphocyte apoptosis. Without the exclusion of these above, it will be difficult to achieve clinical success. At present, most of the clinical trials targeting CD47 are in phase I clinical trials, which mainly focus on hematoma, thus its value in the solid tumors has yet to be verified. In addition, IgG4 antibodies against CD47 do not respond well to solid tumors, even when used in combination with other antibody drugs. Rigorously, pre-clinical assessments of such treatments are warranted. Based on innovative techniques, we expect that CD47 bsAbs discussed in our review will be more extensively and innovatively designed for immunological therapy, therefore facilitating their effectiveness, as well as decreasing immunologically relevant untoward effects. Future research will be required to raise our comprehension of tumor immunology, which will provide important insights into developing more bsAbs.
Author Contributions
YY (1st author) wrote the original draft. ZY and YY (3rd author) revised the manuscript. YY (1st author) prepared tables and figures. YY (3rd author) reviewed and edited. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81703054), Natural Science Foundation of Henan (No. 202300410322), and Training Plan for Young Backbone Teachers in Universities of Henan Province (No. 2020GGJS143).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
1. Thomas B CD, Tzeng V, Baehner L, Boxer A. Treatment of Hairy Cell Leukemia With Recombinant Alpha-Interferon. Blood (1986) 68(2):493–7. doi: 10.1182/blood.V68.2.493.493
2. Ahmed S, Rai KR. Interferon in the Treatment of Hairy-Cell Leukemia. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol (2003) 16:69–81. doi: 10.1016/s1521-6926(02)00084-1
3. Rosenberg A. IL-2: The First Effective Immunotherapy for Human Cancer. J Immunol (2014) 192(12):5451–8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1490019
4. Locy H, de Mey S, de Mey W, De Ridder M, Thielemans K, Maenhout SK. Immunomodulation of the Tumor Microenvironment: Turn Foe Into Friend. Front Immunol (2018) 9:2909. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02909
5. Riley RS, June CH, Langer R, Mitchell MJ. Delivery Technologies for Cancer Immunotherapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov (2019) 18(3):175–96. doi: 10.1038/s41573-018-0006-z
6. Leach DG, Young S, Hartgerink JD. Advances in Immunotherapy Delivery From Implantable and Injectable Biomaterials. Acta Biomater (2019) 88:15–31. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.02.016
7. Velcheti V, Chandwani S, Chen X, Pietanza MC, Burke T. First-Line Pembrolizumab Monotherapy for Metastatic PD-L1-Positive NSCLC: Real-World Analysis of Time on Treatment. Immunotherapy (2019) 11(10):889–901. doi: 10.2217/imt-2019-0061
8. Nisonoff A, Thorbecke GJ. Immunochemistry. Annu Rev Biochem (1964) 33:355–402. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.33.070164.002035
9. Perez P, Hoffman RW, Shaw S, Bluestone JA, Segal DM. Specific Targeting of Cytotoxic T Cells by Anti-T3 Linked to Anti-Target Cell Antibody. Nature (1985) 316(6026):354–6. doi: 10.1038/316354a0
10. Kantarjian H, Stein A, Gökbuget N, Fielding AK, Schuh AC, Ribera JM, et al. Blinatumomab Versus Chemotherapy for Advanced Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. N Engl J Med (2017) 376(9):836–47. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1609783
11. Gökbuget N, Dombret H, Bonifacio M, Reichle A, Graux C, Faul C, et al. Blinatumomab for Minimal Residual Disease in Adults With B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Blood (2018) 131(14):1522–31. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-08-798322
12. Brinkmann U, Kontermann RE. The Making of Bispecific Antibodies. MAbs (2017) 9(2):182–212. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2016.1268307
13. Shim H. Bispecific Antibodies And Antibody-Drug Conjugates for Cancer Therapy: Technological Considerations. Biomolecules (2020) 10(3):360. doi: 10.3390/biom10030360
14. Suurs FV, Lub-de Hooge MN, de Vries EGE, De Groot DJA. A Review of Bispecific Antibodies and Antibody Constructs in Oncology and Clinical Challenges. Pharmacol Ther (2019) 201:103–19. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2019.04.006
15. Wang Q, Chen Y, Park J, Liu X, Hu Y, Wang T, et al. Design and Production of Bispecific Antibodies. Antibodies (Basel) (2019) 8(3):43. doi: 10.3390/antib8030043
16. Spiess C, Zhai Q, Carter PJ. Alternative Molecular Formats and Therapeutic Applications for Bispecific Antibodies. Mol Immunol (2015) 67(2 Pt A):95–106. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2015.01.003
17. Labrijn AF, Janmaat ML, Reichert JM, Parren PWHI. Bispecific Antibodies: A Mechanistic Review of the Pipeline. Nat Rev Drug Discov (2019) 18(8):585–608. doi: 10.1038/s41573-019-0028-1
18. Thakur A, Lum LG. “NextGen” Biologics: Bispecific Antibodies and Emerging Clinical Results. Expert Opin Biol Ther (2016) 16(5):675–88. doi: 10.1517/14712598.2016.1150996
19. Kontermann RE, Brinkmann U. Bispecific Antibodies. Drug Discov Today (2015) 20(7):838–47. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2015.02.008
20. Todoroki K, Mizuno H, Sugiyama E, Toyo’oka T. Bioanalytical Methods for Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies and Antibodydrug Conjugates: A Review of Recent Advances and Future Perspectives. J Pharm BioMed Anal (2020) 179:112991. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2019.112991
21. May C, Sapra P, Gerber HP. Advances in Bispecific Biotherapeutics for the Treatment of Cancer. Biochem Pharmacol (2012) 84(9):1105–12. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2012.07.011
22. Bhutani D, Vaishampayan UN. Monoclonal Antibodies in Oncology Therapeutics: Present and Future Indications. Expert Opin Biol Ther (2013) 13(2):269–82. doi: 10.1517/14712598.2012.758705
23. Minh Ngoc Duong IS. Advances in Bispecific Antibodies Engineering: Novel Concepts for Immunotherapies. J Blood Disord Transfus (2015) 6(1):1–8. doi: 10.4172/2155-9864.1000243
24. Guy DG, Uy GL. Bispecific Antibodies for the Treatment of Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Curr Hematol Malig Rep (2018) 13(6):417–25. doi: 10.1007/s11899-018-0472-8
25. Wang Y, Ni H, Zhou S, He K, Gao Y, Wu W, et al. Tumor-Selective Blockade of CD47 Signaling With a CD47/PD-L1 Bispecific Antibody for Enhanced Anti-Tumor Activity and Limited Toxicity. Cancer Immunol Immunother (2021) 70(2):365–76. doi: 10.1007/s00262-020-02679-5
26. Yun Y GR, Qi C, Youxun L, Pengfei Z, Ziheng Z, et al. A Novel Bispecific Antibody Fusion Protein Co-Targeting EGFR and CD47 With Enhanced Therapeutic Index. Biotechnol Lett (2018) 40(5):789–95. doi: 10.1007/s10529-018-2535-2
27. Matlung HL SK, Barclay NA, van den Berg TK. The CD47-SIRPalpha Signaling Axis as an Innate Immune Checkpoint in Cancer. Immunol Rev (2017) 276:145–64. doi: 10.1111/imr.12527
28. FP L. Molecular Cloning of Integrin-Associated Protein: An Immunoglobulin Family Member With Multiple Membrane-Spanning Domains Implicated in Alpha V Beta 3-Dependent Ligand Binding. J Cell Biol (1993) 123:485–96. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.2.485
29. Brown EJ FW. Integrin-Associated Protein (CD47) and its Ligands. Trends Cell Biol (2001) 11(3):130–5. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(00)01906-1
30. Lymn JS PM, Clunn GF, Rao SJ, Gallagher KL, Hughes AD. Thrombospondin-1 Differentially Induces Chemotaxis and DNA Synthesis of Human Venous Smooth Muscle Cells at the Receptor-Binding Level. J Cell Sci (2002) 115(Pt 22):4353–60. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00119
31. Chung J GA, Frazier WA. Thrombspondin Acts via Integrin-Associated Protein to Activate the Platelet Integrin Alphaiibbeta3. J Biol Chem (1997) 272:14740–6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.23.14740
32. Lindberg FP BD, Caver TE, Gresham HD, Beaudet AL, Brown EJ. Decreased Resistance to Bacterial Infection and Granulocyte Defects in IAP-Deficient Mice. Science (1996) 274:795–8. doi: 10.1126/science.274.5288.795
33. Lim HW, Kwang P, Arwa K, Ryan Allen F, Bernard A. Lack of the Hyaluronan Receptor CD44 Affects the Course of Bacterial Otitis Media and Reduces Leukocyte Recruitment to the Middle Ear. BMC Immunol (2019) 2(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s12865-019-0302-3
34. Ratnikova NM LY, Frolova EI, Kravchenko JE, Chumakov SP. CD47 Receptor as a Primary Target for Cancer Therapy. Mol Biol (2017) 51(2):251–61. doi: 10.7868/S0026898417010153
35. Kim D WJ, Willingham SB, Martin R, Wernig G, Weissman IL. Anti-CD47 Antibodies Promote Phagocytosis and Inhibit the Growth of Human Myeloma Cells. Leukemia (2012) 26(12):2538–45. doi: 10.1038/leu.2012.141
36. Edris B WK, Volkmer AK, Volkmer JP, Willingham SB, Contreras-Trujillo H, et al. Antibody Therapy Targeting the CD47 Protein is Effective in a Model of Aggressive Metastatic Leiomyosarcoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA (2012) 109(17):6656–61. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1121629109
37. Chao MP AA, Tang C, Jan M, Weissman-Tsukamoto R, Zhao F, et al. Therapeutic Antibody Targeting of Cd47 Eliminates Human Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancer Res (2011) 71(4):1374–84. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-2238
38. Chao MP TC, Pachynski RK, Chin R, Majeti R, Weissman IL. Extranodal Dissemination of non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Requires Cd47 and Is Inhibited by Anti-CD47 Antibody Therapy. Blood (2011) 118:4890–901. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-02-338020
39. Willingham SB VJ, Gentles AJ, Sahoo D, Dalerba P, Mitra SS, et al. The CD47-Signal Regulatory Protein Alpha (SIRPa) Interaction Is a Therapeutic Target for Human Solid Tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA (2012) 109(17):6662–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1121623109
40. Mohanty S YK, Theruvath JL, Graef CM, Nejadnik H, Lenkov O, et al. Nanoparticle Enhanced Mri Can Monitor Macrophage Response to Cd47 Mab Immunotherapy in Osteosarcoma. Cell Death Dis (2019) 10(2):36. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-1285-3
41. Liu YC, Lin KH. Cancer Stem Cell Functions in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Comprehensive Therapeutic Strategies. Cells (2020) 9(6):1331. doi: 10.3390/cells9061331
42. Reissfelder C SS, Gossmann C, Braun M, Bonertz A, Walliczek U, et al. Tumor-Specific Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte Activity Determines Colorectal Cancer Patient Prognosis. J Clin Invest (2015) 125(3):739–51. doi: 10.1172/JCI74894
43. Betancur PA AB, Yiu YY, Willingham SB, Khameneh F, Zarnegar M, et al. A CD47-Associated Super-Enhancer Links Pro-Inflammatory Signalling to CD47 Upregulation in Breast Cancer. Nat Commun (2017) 8:14802. doi: 10.1038/ncomms14802
44. Jaiswal S JC, Pang WW, Park CY, Chao MP, Majeti R, et al. CD47 is Upregulated on Circulating Hematopoietic Stem Cells and Leukemia Cells to Avoid Phagocytosis. Cell (2009) 138:271–85. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.05.046
45. Klimp AH dVE, Scherphof GL, Daemen T. A Potential Role of Macrophage Activation in the Treatment of Cancer. Crit Rev Oncol/Hematol (2002) 44(2):143–61. doi: 10.1016/S1040-8428(01)00203-7
46. Wang Y DP, Huang C, Chen B, Li M, Zhou S, et al. Dose Escalation PET Imaging for Safety and Effective Therapy Dose Optimization of a Bispecific Antibody. MAbs (2020) 12(1):1748322. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2020.1748322
47. de Silva S, Fromm G, Shuptrine CW, Johannes K, Patel A, Yoo KJ, et al. CD40 Enhances Type I Interferon Responses Downstream of CD47 Blockade, Bridging Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Cancer Immunol Res (2020) 8(2):230–45. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-19-0493
48. Zhang H, Deng M, Lin P, Liu J, Liu C, Strohl William R, et al. Frontiers and Opportunities: Highlights of the 2(Nd) Annual Conference of the Chinese Antibody Society. Antibody Ther (2018) 1:65–74. doi: 10.1093/abt/tby009
49. Liu X LL, Ren Z, Yang K, Xu H, Luan Y, et al. Dual Targeting of Innate and Adaptive Checkpoints on Tumor Cells Limits Immune Evasion. Cell Rep (2018) 24(8):2101–11. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.07.062
50. Piccione EC, Juarez S, Liu J, Tseng S, Ryan CE, Narayanan C, et al. A Bispecific Antibody Targeting CD47 and CD20 Selectively Binds and Eliminates Dual Antigen Expressing Lymphoma Cells. MAbs (2015) 7(5):946–56. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2015.1062192
51. Tian W SL, Chen D, Liang G, Zhang L, Zhang W, et al. Preclinical Development of a Bispecific Antibody-Trap Selectively Targeting CD47 and CD20 for the Treatment of B Cell Lineage Cancer. In: AACR Annual Meeting 2019. Atlanta GA: American Association for Cancer Research (2019). p. 545. doi: 10.1158/1538-7445.AM2019-545
52. Ma L MZ, Gai J, Li G, Chang Q, Qiao P, et al. Preclinical Development of a Novel CD47 Nanobody With Less Toxicity and Enhanced Anti-Cancer Therapeutic Potential. J Nanobiotech (2020) 18(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s12951-020-0571-2
53. Dheilly E VM, Broyer L, Salgado-Pires S, Johnson Z, Papaioannou A, et al. Selective Blockade of the Ubiquitous Checkpoint Receptor CD47 Is Enabled by Dual-Targeting Bispecific Antibodies. Mol Ther (2017) 25(2):523–33. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2016.11.006
54. Lunning M JV, Nastoupil L, Fowler N, Burger JA, Wierda WG, et al. Ublituximab and Umbralisib in Relapsed_Refractory B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma and Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Blood (2019) 134(21):1811–20. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019002118
55. Ribeiro ML EN, Garau DR, Miskin HP, Sportelli P, Weiss MS, et al. The Novel Bispecific CD47-CD19 Antibody TG-1801 Potentiates the Activity of Ublituximab-Umbralisib (U2) Drug Combination in Preclinical Models of B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Hematol Oncol (2019) 37(S2):322–3. doi: 10.1002/hon.133_2630
56. Fromm G dSS, Johannes K, Patel A, Hornblower JC, Schreiber TH. Agonist Redirected Checkpoint, PD1-Fc-OX40L, for Cancer Immunotherapy. J Immunother Cancer (2018) 6(1):149. doi: 10.1186/s40425-018-0454-3
57. Chao MP SJ, Weissman-Tsukamoto R, Alizadeh AA, Gentles AJ, Volkmer J, et al. Calreticulin is the Dominant Pro-Phagocytic Signal on Multiple Human Cancers and is Counterbalanced by CD47. Sci Transl Med (2010) 2(63):63ra94. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3001375
58. Chao MP, Alizadeh Ash A, Tang C, Myklebust JH, Varghese B, Gill S, et al. Anti-CD47 Antibody Synergizes With Rituximab to Promote Phagocytosis and Eradicate Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Cell (2010) 142(5):699–713. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.07.044
59. Oldenborg PA ZA, Fang YF, Lagenaur CF, Gresham HD, Lindberg FP. Role of CD47 as a Marker of Self on Red Blood Cells. Science (2000) 288(5473):2051–4. doi: 10.1126/science.288.5473.2051
60. Buatois V, Johnson Z, Salgado-Pires S, Papaioannou A, Hatterer E, Chauchet X, et al. Preclinical Development of a Bispecific Antibody That Safely and Effectively Targets CD19 and CD47 for the Treatment of B-Cell Lymphoma and Leukemia. Mol Cancer Ther (2018) 17(8):1739–51. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-17-1095
61. Sikic BI LN, Patnaik A, Shah SA, Chandana SR, Rasco D, et al. First-In-Human, First-in-Class Phase I Trial of the Anti-CD47 Antibody Hu5F9-G4 in Patients With Advanced Cancers. J Clin Oncol (2019) 37(12):946–53. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.02018
62. Ansell SM MM, Lesokhin AM, Chen RW, Flinn IW, Sawas A, et al. Phase I Study of the CD47 Blocker TTI-621 in Patients With Relapsed or Refractory Hematologic Malignancies. Clin Cancer Res (2021) 27(8):2190–9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-3706
63. Advani R, Flinn I, Popplewell L, Forero A, Bartlett NL, Ghosh N, et al. CD47 Blockade by Hu5F9-G4 and Rituximab in Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. N Engl J Med (2018) 379(18):1711–21. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1807315
64. Weiskopf K RA, Ho CC, Volkmer JP, Levin AM, Volkmer AK, et al. Engineered SIRPα Variants as Immunotherapeutic Adjuvants to Anticancer Antibodies. Science (2013) 341(6141):88–91. doi: 10.1126/science.1238856
65. Liu J WL, Zhao F, Tseng S, Narayanan C, Shura L, et al. Pre-Clinical Development of a Humanized Anti-CD47 Antibody With Anti-Cancer Therapeutic Potential. PloS One (2015) 10(9):e0137345. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137345
66. Tseng D VJ, Willingham SB, Contreras-Trujillo H, Fathman JW, Fernhoff NB, et al. Anti-CD47 Antibody-Mediated Phagocytosis of Cancer by Macrophages Primes an Effective Antitumor T-Cell Response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA (2013) 110(27):11103–8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1305569110
67. Liu X PY, Cron K, Deng L, Kline J, Frazier WA, et al. CD47 Blockade Triggers T Cell-Mediated Destruction of Immunogenic Tumors. Nat Med (2015) 21(10):1209–15. doi: 10.1038/nm.3931
68. Sockolosky JT DM, Ingram JR, Ho CC, Kauke MJ, Almo SC, et al. Durable Antitumor Responses to CD47 Blockade Require Adaptive Immune Stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA (2016) 113(19):E2646–54. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1604268113
69. Gordon SR MR, Dulken BW, Hutter G, George BM, McCracken MN, et al. PD-1 Expression by Tumour-Associated Macrophages Inhibits Phagocytosis and Tumour Immunity. Nature (2017) 545(7655):495–9. doi: 10.1038/nature22396
70. Liu B GH, Xu J, Qin T, Guo Q, Gu N, et al. Elimination of Tumor by CD47/PD-L1 Dual-Targeting Fusion Protein That Engages Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses. MAbs (2018) 10(2):315–24. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2017.1409319
Keywords: cancer immunotherapy, bispecific antibodies (bsAbs), CD47, immune checkpoint, macrophage, phagocytosis
Citation: Yang Y, Yang Z and Yang Y (2021) Potential Role of CD47-Directed Bispecific Antibodies in Cancer Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 12:686031. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.686031
Received: 26 March 2021; Accepted: 28 June 2021;
Published: 08 July 2021.
Edited by:
Xiangqian Guo, Henan University, ChinaReviewed by:
Shaoping Ji, Henan University, ChinaYinan Jiang, University of Pittsburgh, United States
Copyright © 2021 Yang, Yang and Yang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yun Yang, jamesyangyun1@126.com
 Yan Yang
Yan Yang Zheng Yang2
Zheng Yang2 Yun Yang
Yun Yang