Intestinal parasites infection and associated factors among school children in Dagi primary school, Amhara National Regional State, Ethiopia ()
1. INTRODUCTION
Intestinal parasitic infections are among the most common communicable diseases worldwide, particularly in developing countries. Worldwide, about 3.5 billion people are affected, and 450 million are ill as a result of these infections, the majority being children [1]. Parasitic infections, caused by intestinal helminthes and protozoan parasites, are among the most prevalent infections in humans in developing countries and cause significant morbidity and mortality, iron deficiency anemia, growth retardation in children and other physical and mental health problems in endemic countries [2,3].
In Ethiopia, the major health problems of the country are largely preventable communicable diseases and nutritional disorders [4]. Life expectancy at birth of males and females is 49.7 years and 52.4 years respectively. The total burden of disease, as measured by premature death from all causes, is approximately 350 deaths per year lost per 1000 populations, which is higher than Kenya [5].
Previous research works in Ethiopia showed that there was a high prevalence rate of intestinal parasites infection among students; 83.8% in a rural area close to the southeast of Lake Langano [6], 85.1% among children of under five years old in Wondo Genet, Southern Ethiopia [7], 82.4% in Zarima town, northwest Ethiopia [8]. The objective of this study was to assess prevalence of intestinal parasite infection and associated risk factors among school children in Dagi primary school, Ethiopia.
2. METHODS
2.1. Study Design
A cross-sectional study was conducted from 24 September to 19 October, 2012 among school children in Dagi primary school, ANRS, Ethiopia. There were a total of 1780 (980 female and 800 male) school children attending from 1 to 8 grade levels. All school children from grade 2 to 8 were included in the sample. Grade one students were excluded from the study because of the de-worming program that was launched by the Federal Ministry of Health, Ethiopia.
Sampling Size and Sampling Procedure
The sample size was determined by using single population proportion formula based on the following assumptions, prevalence of intestinal parasites infection among school children (P = 79%) reported from other studies in elsewhere in Ethiopia [9], 95% confidence interval and (4%) marginal error and by adding 10% compositions for the non-response rate. The final sample size was calculated to be 439 students. Then, the sample size was proportionally distributed according to number of students in each grade level. Finally, in each grade level, students were selected randomly using list of students as sampling frame.
2.2. Data Collection Tool and Management
A structured questionnaire was prepared originally in English according to the research objectives and the local situation and then was translated in to the local Amharic language. Six data collectors who completed grade 10 and two supervisors having diploma in clinical nursing were recruited for data collection and supervision respectively. Two laboratory technicians were recruited for stool collections and laboratory examinations. Training for data collectors and supervisors was given for one day, mainly on the objective of the study, the procedure of data collection and handling of ethical issues. The questionnaires were pretested in Gibacha primary which is located in the nearby area and having similar characteristics and correction was made accordingly. The selected students were asked using the revised and standardized questionnaires and the presence of intestinal parasites in each student was checked by using direct microscopic examination and formal-ether concentration technique.
The collected data was coded and entered in to a statistical package of SPSS version 15. Bivariate and multiple logistic regression analysis were done; Adjusted Odds Ratio with 95% Confidence Intervals was calculated to test the strength of the association. P-Values ≤ 0.05 were considered as statistically significant.
2.3. Ethical Consideration
Ethical clearance was obtained from the Ethical Committee of Bahir Dar University and letters for permission was gained from Amhara National Regional State Health Bureau, Zonal Health department and District Health Office. The study subjects were informed about the objective of the study and all the reasons why participants were chosen and why the research was to be done were explained in the questionnaires. The participants were allowed to consider their participation and given the opportunity to withdraw from the study at any point in the course of the study if they wished to do so. Additionally confidentiality of all the information was assured.
3. RESULT
3.1. Socio Demographic Characteristics
A total of 399 students from grade 2 - 6 were enrolled in the study. All 399 students gave stool samples and interviewed standardized and pre-tested questionnaires. Out of 399 students, 209 (52.1%) were females, 183 (45.9%) were in the age group of 12 - 14 years, 375 (94%) were Orthodox Christian by religion and 374 (93.7%) were from Amhara ethnic group. Pertaining to socio demographic characteristics of the parents, 263 (65.9%) of fathers and 299 (74.9%) of the mothers were illiterate, 315 (78.5%) of fathers and 369 (92.5%) of mothers were farmers by their occupational status (Table 1).
3.2. Intestinal Parasite Infections
Eight species of intestinal parasites were identified with an overall prevalence of 77.9% (311 out of 399). Students were infected with one or more intestinal parasites. From the total of 311students with intestinal parasite infection, mixed parasitic infection was observed in 95 (28.5%) students. The predominant parasite was hook worm which was observed in 94 (23.6%) of the students; followed by 91 (22.8%) G. lamblia, 86 (21.6%) E. histolytica, 66 (16.8%) A. lumbricoides, 33 (8.3%) E. vermicularis, 28 (7%) Taenia species and 6 (1.5%) Strongyloides (Table 2).
3.3. Factors Associated with Intestinal Parasites Infection
Among the potential risk factors explored using

Table 1.Socio-demographic characteristics of students, Dagi primary school, ANRS, Ethiopia, 2012 (n = 399).
bivariate logistic regression analysis, fathers’ occupational status, source of water for drinking for the households, habit of purifying water before drinking, hand washing habit, hand washing with soap/ash, cleanliness of finger were statistically significant with intestinal parasitic at P-value less than 0.05. Finally those significant variables were entered to multivariate analysis. From the potential risk factors associated with intestinal parasitic infections in bivariate analysis; hand washing habit, cleanness of finger nails and shoes’ wearing habits were continued significantly associated with intestinal parasitic infection in the multivariate analysis (Table 3).
In addition, hand washing habit was significantly associated with intestinal parasitic infections; those students who washed their hands only before meal were 10 times more likely to acquire intestinal parasitic infection as compared to those who washed their hands both before meal and after defecations (AOR = 10.56; 95% CI:
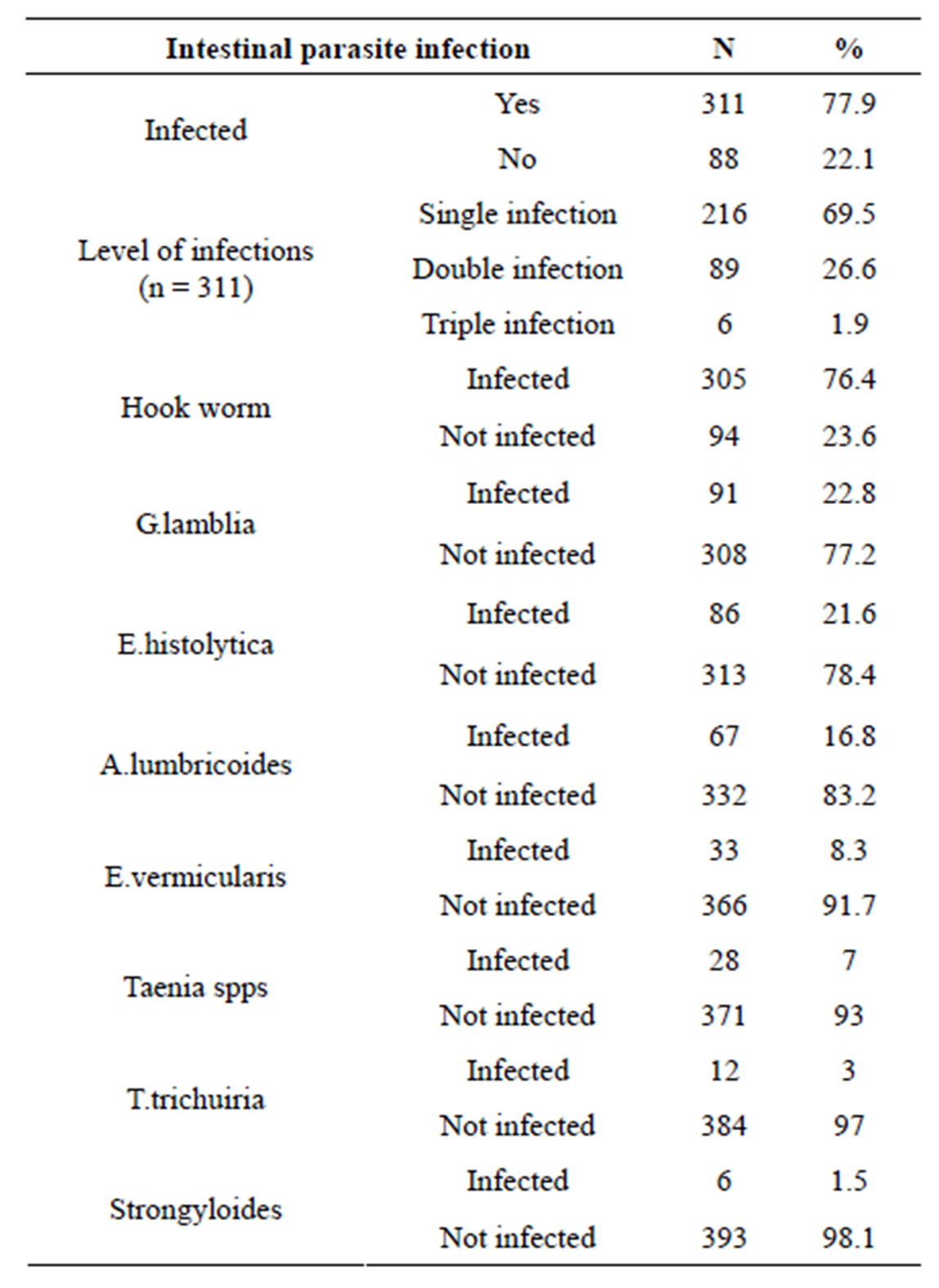
Table 2. Intestinal parasitic infections among school children, Dagi primary school, ANRS, Ethiopia, in 2012 (n = 399).
4.827, 23.12). Similarly students who had no clean finger nails (AOR = 3.281; 95% CI: 1.871, 6.015) and had not wearing shoes habit (AOR = 2.71; 95% CI: 1.491, 4.971) 3.3 and 2.7 times more likely to acquire intestinal parasitic infection as compared to those who had wearing shoes habit and clean finger nail respectively (Table 3).
4. DISCUSSION
The overall prevalence of intestinal parasites infection among students of Dagi primary school was 77.9%. This was comparable with 82.4% in Zarima [8], 78.8% in Delgi [9], 73.3% in Malaysia, [10]. In this study the most prevalent infection was hook worm and the least (23.6%) prevalent infections were Strongyloides (1.5) Those children who washed their hands before meal only were 10 times more likely to acquire intestinal parasite than those who wash their hands after defecation with p - value 0.001 (AOR = 10.56; 95% CI: 4.827 - 23.125). Study conducted among school children on prevalence of intestinal parasites in AL-Ahsa, Saudi Arabia showed that hand washing habit before meal and following defecation and the material used to wash their hands were significantly associated with increased risk to infection (AOR = 1.52, 95% CI; 0.72 - 3.22, P = 0.0168), [11].
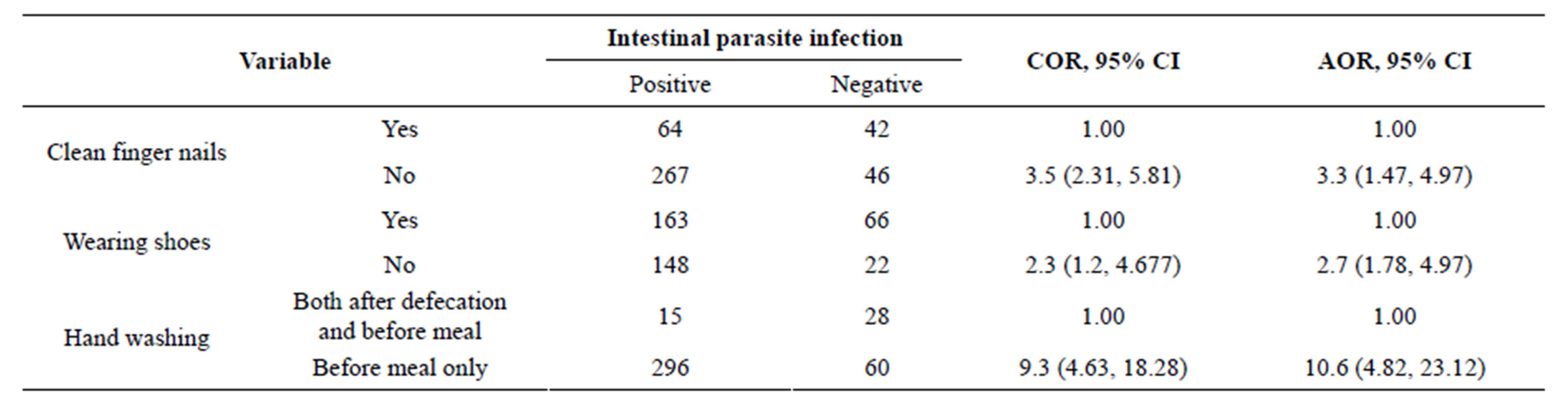
Table 3. Factors associated with Intestinal parasitic infections among school children, Dagi primary school, ANRS, Ethiopia, in 2012 (n = 399).
Similar to this findings, Study conducted on prevalence of intestinal parasite infections among school children in Zarima town, North West Ethiopia showed that hand washing habit with soap was significantly associated with children intestinal parasitic infection, increased risk was seen in those who washed their hands with water only (overall P = 0.000, AOR = 5.03; 95% CI: 1.43 - 20.23) [8].
Similar to this findings, another study conducted on prevalence of intestinal parasite and associated risk factors among Delgi primary school children in North Gondar, Ethiopia showed that children who washed their hands before meal only (AOR = 3.88; 95% CI: 2.46 - 6.08) were more likely to acquire intestinal parasite infections than children who washed their hands both before meal and after defecation [9]. From the observational variables, students who had no clean finger nails (AOR = 3.3; 95% CI; 1.789, 6.015) and had not habit of wearing shoes (AOR = 2.7; 95% CI: 1.479, 4.971) were 3.3 and 2.7 time more likely to acquire intestinal parasitic infections as compared to those who had clean finger nails and wearing shoes habit respectively. Similar to this findings study conducted in Zarima town Ethiopia showed that students who had not habit of wearing shoes were infected with intestinal parasites (P < 0.05) [8].
5. CONCLUSIONS
Intestinal parasitic infections were highly prevalent health problem among school children in Dagi primary school. The risk factor of the prevalence of intestinal parasites was hand washing habit before meals and after defecations. In addition to this, prevalence of intestinal parasite infections was also shown a significant association among children having unclean finger nails, and did not wear shoes. All these factors including hand washing habit with soap or ash before meals and after defecations, and keeping finger nails clean plays an important role in preventing children from infection of intestinal parasites. Habit of wearing shoes was found to be a protective factor for hook worm infection.
Therefore, the local District Health Office and other governmental and non-governmental organizations need to give attention to this serious problem of intestinal parasitic infection of school children. School children should be provided with school based health information with special emphasis on the importance of personal hygiene and the habit of wearing shoes in case of intestinal parasitic infection.
6. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We would like to acknowledge Bahir Dar University, GAMBY College of Medical Sciences, students and staffs of Dagi primary school staffs, all data collectors and supervisors.